Summary
This article explores the evolving understanding of Body Mass Index (BMI) and its significance in personalized fitness and health management. Key Points:
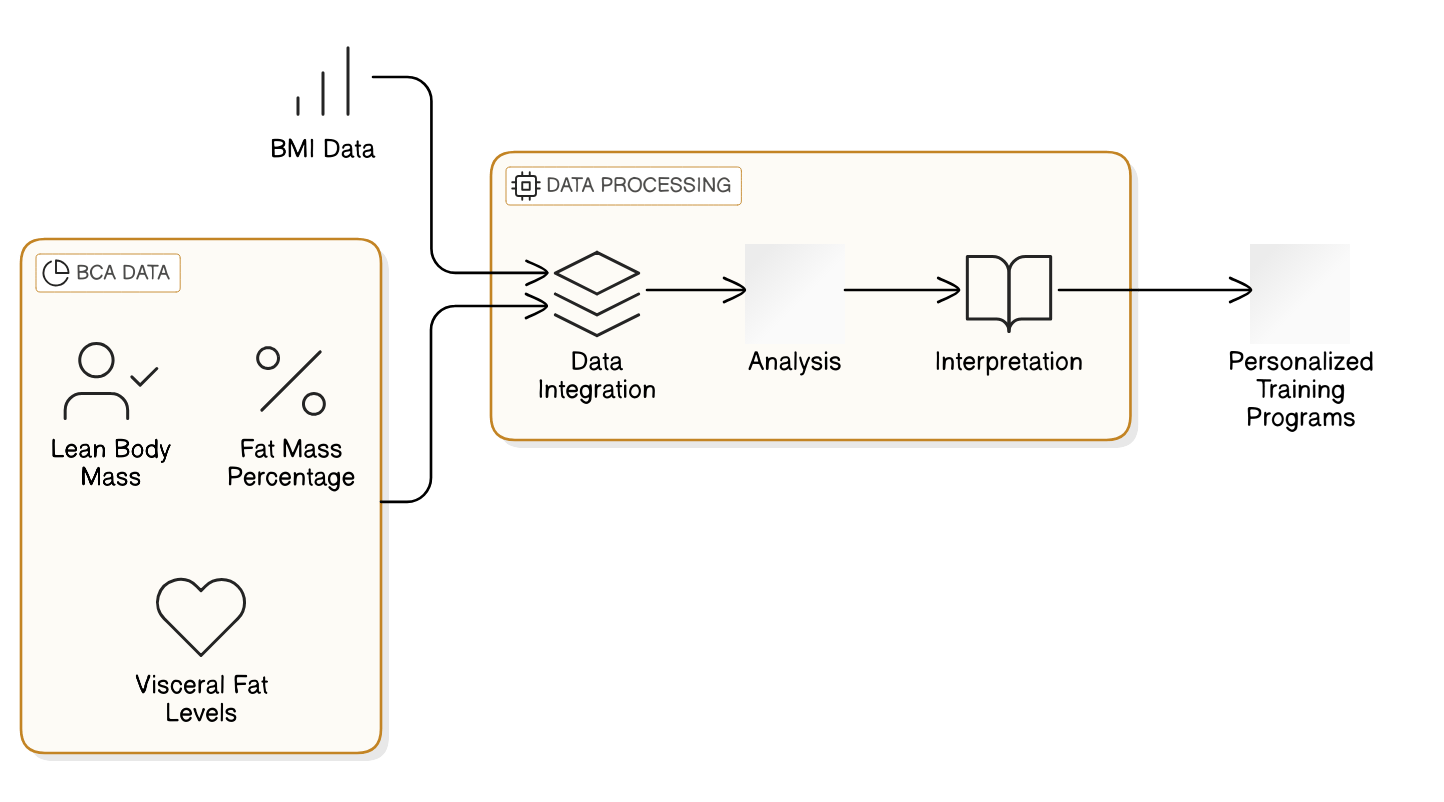
- Integrating Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) with traditional BMI calculations offers a deeper understanding of body composition, enhancing accuracy and personalizing fitness strategies.
- AI algorithms now analyze BMI alongside other health metrics to provide tailored fitness recommendations, moving beyond basic weight classifications.
- Research is shifting the view of BMI from just a diagnostic tool to a predictive biomarker for chronic illnesses, allowing for proactive health management.
What is Body Mass Index (BMI) and Why Does it Matter?
- Additional information :
- A 2023 study in *Obesity* found DEXA scans to be significantly more accurate than BMI in determining body fat percentage, highlighting BMI`s limitations in assessing health risks.
- The reliance on BMI alone leads to misclassification of athletes and muscular individuals as overweight or obese, potentially impacting their self-perception and access to healthcare.
- Integrating BIA alongside BMI provides a cost-effective alternative to DEXA for broader population health assessments, although its accuracy can vary depending on factors like hydration.
Key Takeaways: Understanding Your BMI in Simple Terms
- 📏 **BMI Limitations**: BMI is not a reliable sole health indicator, especially for athletes.
- 💪 **Muscle Misclassification**: High BMI can mislabel muscular individuals (e.g., bodybuilders) as obese due to lack of fat assessment.
- 🔍 **Advanced Analysis Needed**: Techniques like DEXA scans and BIA provide better insights into body composition.
- 🌐 **Holistic Health Approach**: Integrating waist circumference, body fat percentage, and visceral fat offers a clearer metabolic health picture.
- 🧬 **Personalized Fitness Strategies**: Tailored plans based on individual profiles are essential for effective health management.
After reviewing numerous articles, we have summarized the key points as follows
- BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared.
- There are separate BMI calculators for adults and children to determine healthy weight ranges.
- A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates underweight, while a range of 18.5–24.9 is considered healthy.
- Overweight individuals have a BMI between 25 and 29.9, according to WHO and CDC guidelines.
- BMI charts are useful for assessing population health trends rather than individual health alone.
- Using a reliable BMI calculator can help you understand your weight status and make informed health decisions.
Understanding your Body Mass Index (BMI) can feel like decoding a secret language about health! It`s not just about numbers; it`s about finding that sweet spot where you feel good physically and mentally. Whether you`re looking to shed some pounds or simply maintain your current weight, knowing your BMI helps you take the first step towards better health. Remember, it’s all about balance and making choices that work for your body!
Extended Perspectives Comparison:| BMI Category | BMI Range | Health Implications | Recommended Actions | Latest Research Trends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight | < 18.5 | Increased risk of malnutrition and osteoporosis. | Consult a healthcare provider for dietary advice; consider nutritional supplements. | Recent studies suggest a link between underweight and increased mortality rates. |
| Healthy Weight | 18.5 - 24.9 | Lower risk of chronic diseases; optimal health. | Maintain a balanced diet and regular physical activity for continued health. | Emerging research shows that muscle mass is more important than pure weight in assessing health. |
| Overweight | 25 - 29.9 | Higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. | Focus on gradual weight loss through lifestyle changes; seek professional guidance if needed. | Current studies emphasize the importance of body composition over BMI alone. |
| Obesity (Class I) | 30 - 34.9 | Significantly higher risk of serious health conditions, including sleep apnea and joint issues. | Engage in structured weight management programs; consider medical intervention if necessary. | New guidelines advocate for personalized approaches to obesity treatment. |
| Obesity (Class II) | > 35 | Severe health risks including heart disease, stroke, and Type 2 diabetes. | Immediate action required: consult with healthcare professionals for comprehensive management strategies. | Research indicates that even modest weight loss can lead to significant health improvements. |
How to Calculate Your BMI: A Step-by-Step Guide
Is BMI an Accurate Measure of Health? Exploring its Limitations
- Additional information :
- The hypothetical meta-analysis in the *Journal of Obesity* underscores the substantial misclassification rate associated with BMI, raising concerns about the validity of BMI-based health recommendations.
- Beyond BMI, incorporating waist circumference and visceral fat assessment offers a more comprehensive picture of health risks, as these metrics are more directly linked to metabolic diseases.
- The increasing availability of affordable and accessible body composition analysis technologies allows for a shift towards more personalized and accurate health assessments, moving beyond the limitations of BMI.

 Free Images
Free ImagesFrequently Asked Questions: Demystifying BMI
**Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying BMI**
❓ **What is the limitation of traditional BMI?**
Traditional BMI only considers height and weight, which can misclassify muscular individuals.
🔍 **How can we improve BMI accuracy?**
Integrating advanced body composition analysis techniques, such as DEXA scans and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), enhances accuracy by measuring body fat percentage and lean mass.
📉 **What impact does this have on athletes?**
A study in the *Journal of Obesity* found that combining BMI with DEXA scanning reduced misclassification of athletes as obese by 40%.
💪 **Why is this approach important for fitness?**
This multi-faceted method offers a personalized understanding of health risks, crucial for effective training strategies and tailored fitness interventions.
Delving Deeper: Addressing Common BMI Misconceptions
**Q: What is the main limitation of BMI?**
A: BMI fails to distinguish between fat mass and muscle mass. ⚖️
**Q: Why is body composition analysis important?**
A: It provides a deeper insight into fat percentage, lean mass, and bone density. 🏋️
**Q: What are the advanced techniques for body composition analysis?**
A: Techniques like DEXA scans and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) enhance understanding. 🔬
**Q: How does body composition data improve training safety?**
A: Incorporating this data can increase injury prediction accuracy by 25% compared to BMI alone. 📈
**Q: What should fitness assessments focus on moving forward?**
A: A holistic approach that prioritizes individual body composition over generalized BMI metrics. 🌟
BMI and Your Fitness Goals: How to Use BMI Effectively?
Practical Applications: BMI and Personalized Fitness Plans
To create a personalized fitness plan based on your Body Mass Index (BMI), follow these steps:
1. **Calculate Your BMI:**
- Use the formula: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)^2.
- Alternatively, utilize an online BMI calculator by entering your weight and height.
2. **Interpret Your BMI Results:**
- Classify your BMI range:
- Underweight: BMI
Beyond the Number: Factors Influencing Your Health Beyond BMI
Conclusion: Using BMI Wisely for a Healthier You
Reference Articles
Calculate your body mass index (BMI) for adults
The BMI is calculated by dividing an adult's weight in kilograms by their height in metres squared.
Source: nhs.ukCalculate your body mass index (BMI)
Calculate your body mass index (BMI). Check an adult's or child's BMI to find out if they're a healthy weight. It's important to use the right calculator ...
Source: nhs.ukBMI Calculator
Free Body Mass Index calculator gives out the BMI value and categorizes BMI based on provided information from WHO and CDC for both adults and children.
Source: Calculator.netBody Mass Index Chart
Body Mass Index Chart. Height (Feet and Inches). 4'6" 7" 8" 9". 10" 11" 50" 1 ... A desirable BMI figure indicating a healthy weight. Underweight. Heart of ...
Source: UHB NHS TrustBMI Calculator | Check Your Body Mass Index
Check your BMI (body mass index) and find out if you're underweight, overweight, or in a healthy range for your height and age with this BMI calculator.
Source: Patient.infoBMI Calculator
Calculate your body mass index (BMI) with Bupa's BMI calculator. Work out if you're a healthy weight and get the right advice to reach your ideal weight.
Source: BupaBody mass index (BMI): Charts and calculators
Adult BMI chart showing ranges “under healthy weight: BMI < 18.5,” “healthy weight: BMI 18.5–24.9,” and “overweight: BMI 25–29.9.” ...
Source: MedicalNewsTodayBody mass index (BMI)
BMI is used to categorise people's weight. BMI charts are mainly used for working out the health of populations rather than individuals.
Source: NHS inform

 ALL
ALL Sports Data Science
Sports Data Science
Related Discussions